Sexual Reproduction
Sexual Reproduction: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Sexual Reproduction, Events in Sexual Reproduction, Pre-fertilization Events, Cell Division during Gamete Formation, Gamete Transfer, Fertilization, Parthenogenesis, Post Fertilization Events, Zygote, etc.
Important Questions on Sexual Reproduction
Earthworms are hermaphrodite animals.
A male honey bee has _____ chromosomes whereas its female has 32 chromosomes.
In bee society, all the members are diploid except drones.
The mode of sexual reproduction in bacteria is by conjugation.
ll organisms have to pass through a particular phase before they can reproduce sexually. What do we call this phase?
Name the kind of reproduction in the bees in which drones are produced, whether it is parthenogenesis or sexual reproduction?
The term 'clone' cannot be applied to offspring formed by sexual reproduction because
What is the function of the pericarp in the fruit?
What is the term given to the point of attachment of the ovules in the fruit?
Name the parts from which the seed and pericarp develop.
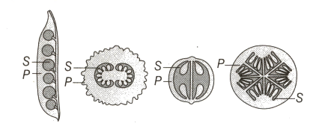
Answer the following questions based on the figures given below.
What do S and P denote?
Name the reproductive cycle that occurs in non-primates. (Answer in two words.)
Embryogenesis involves several processes. Identify the process that is responsible for the formation of different types of tissues.
Embryogenesis involves several processes. Identify the process that increases the number of cells.
Identify the statements as correct/incorrect and give proper justification for your answer.
Zygote is a single cell.
Name the carrier of male gametes in seed producing plants.
Mention the fate of ovule and ovary after syngamy.
Name the largest cell of the embryo sac.
Choose correct pair from the given below related to the study of fertilization.
| A | Aquatic algae | Large no. of gametes released into the surrounding medium | External Syngamy |
| B | Moss plants | Large no. of gametes released into air | External Syngamy |
| C | Seed plants | Non motile male gamete reach the egg | Internal Syngamy |
| D | Pteridophytes | Motile male gamete reach the egg | Internal Syngamy |